Eating a variety of whole (i.e. unprocessed) and fresh foods every day helps children and adults to obtain the right amounts of essential nutrients.
It also helps them to avoid a diet that is high in sugars, fats and salt, which can lead to unhealthy weight gain (i.e. overweight and obesity) and noncommunicable diseases. Eating a healthy, balanced diet is especially important for young children’s development. It also helps older people to have healthier and more active lives.
WHO recommends that people eat a combination of different foods, including staple foods (e.g. cereals such as wheat, barley, rye, maize or rice, or starchy tubers or roots such as potato, yam, taro or cassava), legumes (e.g. lentils, beans), vegetables, fruit and foods from animals sources (e.g. meat, fish, eggs and milk).
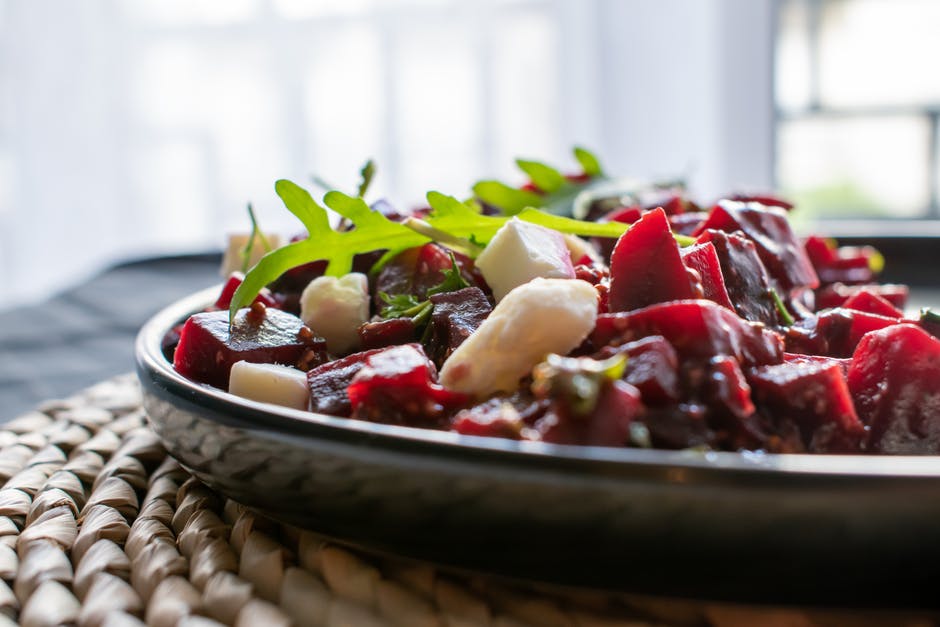
Plenty of vegetables
WHO recommends that people eat a wide variety of vegetables and fruit. For snacks, choose raw vegetables and fresh fruit, rather than foods that are high in sugars, fats or salt.
Avoid overcooking vegetables and fruit as this can lead to the loss of important vitamins. When using canned or dried vegetables and fruit, choose varieties without added salt and sugars
Vegetables and fruit are important sources of vitamins, minerals, dietary fibre, plant protein and antioxidants. People whose diets are rich in vegetables and fruit have a significantly lower risk of obesity, heart disease, stroke, diabetes and certain types of cancer.
Source: WHO