Benefits of breastfeeding outweigh potential risks
The COVID-19 virus has not been detected in the breastmilk of any mother with confirmed and suspected COVID-19 and there is no evidence so far that the virus is transmitted through breastfeeding. Researchers continue to test breastmilk from mothers with the infection.
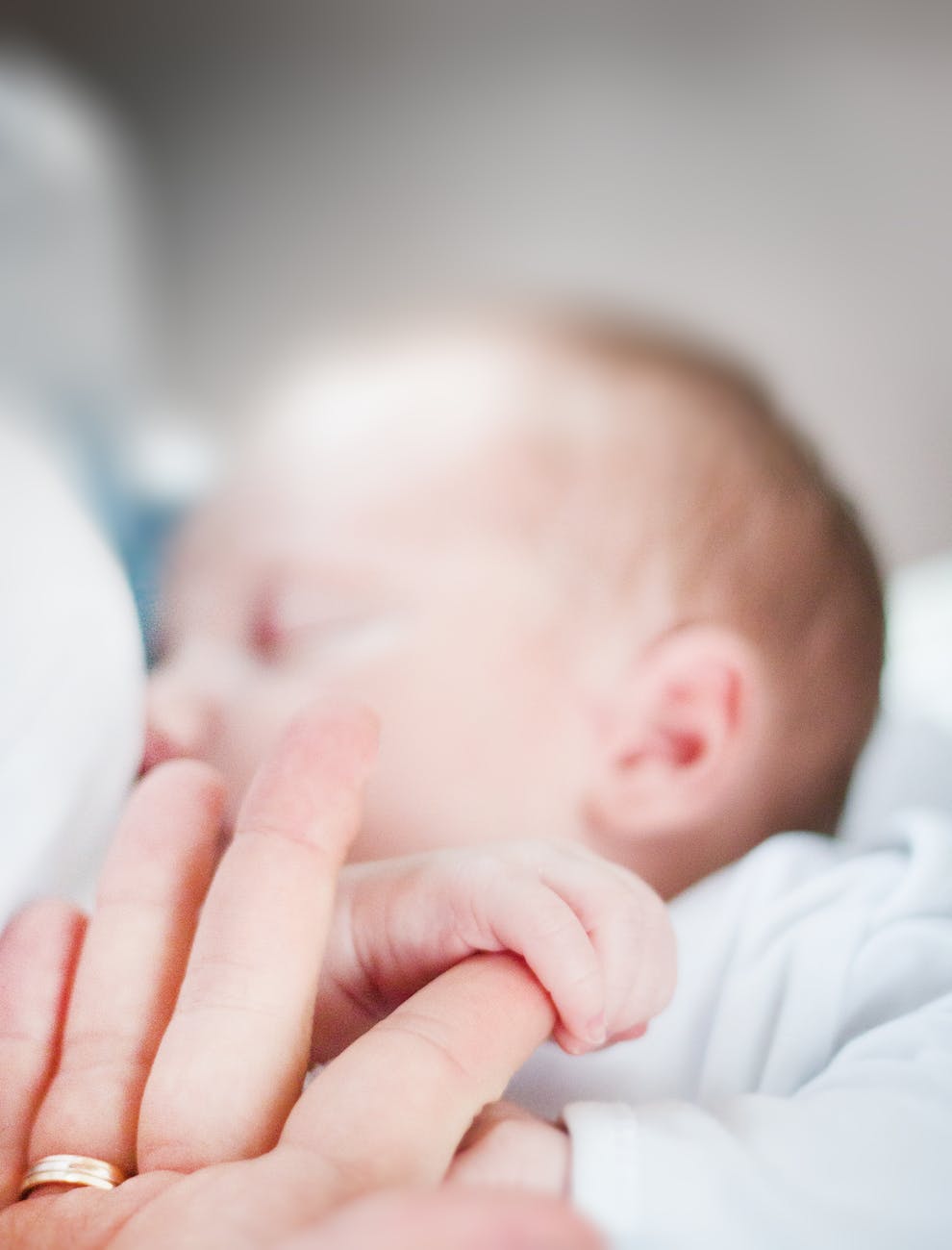
WHO recommends that all mothers with confirmed or suspected COVID-19 continue to have skin-to-skin contact and to breastfeed. In all socio-economic settings, breastfeeding improves survival and provides lifelong health and development advantages to newborns and infants. Breastfeeding also reduces the risk of breast and ovarian cancer for the mother. Skin-to-skin contact, including kangaroo mother care, reduces neonatal mortality, especially for low birth weight newborns.
While infants and children can contract COVID-19, they are at low risk of infection. The few confirmed cases of COVID-19 in young children to date have experienced only mild or asymptomatic illness.
Yes. Immediate and continued skin-to-skin care, including kangaroo mother care, improves the temperature control of newborns and is associated with improved survival among newborn babies. Placing the newborn close to the mother also enables early initiation of breastfeeding which also reduces mortality.
The numerous benefits of skin-to-skin contact and breastfeeding substantially outweigh the potential risks of transmission and illness associated with COVID-19.
Source: WHO